Understanding Passive House Buildings: The Future of Sustainable Living

In the world of sustainable architecture, Passive House buildings stand out as a beacon of energy efficiency and comfort. These buildings, known for their rigorous standards and impressive performance, offer a glimpse into the future of eco-friendly living. Let’s delve into what Passive House buildings are, their benefits, and why they are becoming a preferred choice for homeowners and builders alike.
What is a Passive House?
A Passive House (or Passivhaus) is a building standard that emphasizes superior energy efficiency, comfort, and indoor air quality. Developed in Germany in the late 1980s, the Passive House standard focuses on reducing the need for heating and cooling through careful design and construction.
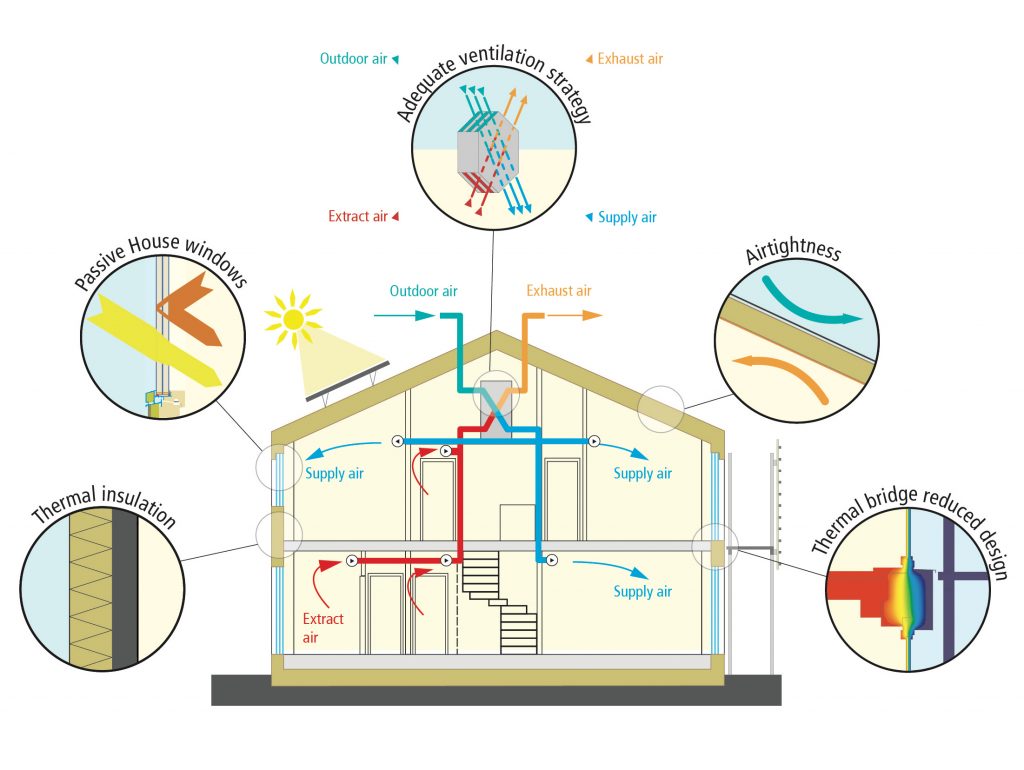
Key features of a Passive House include:
- High Insulation: Walls, roofs, and floors are highly insulated to minimize heat loss.
- Airtight Construction: Building envelopes are designed to be extremely airtight, reducing drafts and heat loss.
- High-Performance Windows: Triple-pane windows and insulated frames help maintain consistent indoor temperatures.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation: These systems recover heat from outgoing air to warm incoming fresh air, drastically improving energy efficiency.
- Thermal Bridge-Free Construction: Special techniques are used to eliminate thermal bridges, where heat can bypass insulation and escape.
Benefits of Passive House Buildings
The Passive House standard offers numerous benefits, making it an attractive option for both homeowners and municipalities:
- Energy Savings: Passive House buildings consume up to 90% less heating and cooling energy compared to conventional buildings, resulting in significantly lower energy bills.
- Comfort: Due to their superior insulation and ventilation, Passive House buildings maintain consistent indoor temperatures and excellent air quality, creating a more comfortable living environment.
- Environmental Impact: By drastically reducing energy consumption, Passive House buildings contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change.
- Durability and Resilience: The high-quality construction and materials used in Passive House buildings ensure they are durable and resilient to external weather conditions.
How Passive House Buildings Work
The remarkable efficiency of Passive House buildings is achieved through several innovative design principles:
- Superinsulation: By using thick layers of insulation in walls, roofs, and floors, Passive Houses minimize heat loss during winter and heat gain during summer. This insulation helps maintain a stable indoor temperature year-round.
- Airtightness: A key aspect of Passive House design is creating an airtight building envelope. This prevents unwanted air leakage, which can account for a significant portion of energy loss in traditional buildings.
- High-Performance Windows and Doors: Passive House windows are typically triple-glazed with insulated frames, significantly reducing heat transfer. Properly installed, these windows and doors contribute to the building’s overall airtightness and insulation.
- Ventilation with Heat Recovery: Mechanical ventilation systems with heat recovery (MVHR) ensure a constant supply of fresh air while capturing and reusing heat from the outgoing stale air. This not only improves indoor air quality but also reduces the energy needed for heating.
- Thermal Bridge-Free Construction: Thermal bridges occur when there are gaps in the insulation, allowing heat to escape. Passive Houses are designed to eliminate these gaps, ensuring that the insulation performs effectively.
The Growing Popularity of Passive House
As awareness of climate change and environmental sustainability grows, so does the popularity of Passive House buildings. Homeowners and developers are increasingly recognizing the long-term benefits of these energy-efficient homes. Not only do they offer substantial savings on energy bills, but they also provide a healthier and more comfortable living environment.
Moreover, the Passive House standard is not limited to residential buildings. It is being successfully applied to schools, offices, and commercial buildings, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness across various building types.
Conclusion
Passive House buildings represent a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable living. By combining cutting-edge design principles with a focus on energy efficiency and comfort, these buildings offer a viable solution to many of the environmental challenges we face today. As the demand for green building solutions continues to rise, Passive House stands out as a leading standard for creating homes and buildings that are not only environmentally friendly but also economical and enjoyable to live in.
Embracing Passive House principles is a commitment to a sustainable future—one where comfort, efficiency, and environmental responsibility go hand in hand.